Data Privacy: 3 Examples Why Contact Tracing Is More Secure Than Its Reputation
When it comes to strategic contact tracing, there is no way around a discussion on data protection. Three prejudices are particularly common. We clarify.
The topic of contact tracing rarely gets by without a discussion of data protection. However, there are important concerns and questions that can be clearly and easily resolved:
1
Does contact tracing impact privacy?
The aim of contact tracing is exclusively to inform people whether they have had infection-critical contact with a COVID-19-infected person and if so, to interrupt the chain of infection.
Technical solutions such as our KINEXON SafeZone follow the principle of voluntary contact tracing. This means that users are not restricted in their personal rights, but are given the opportunity to have their rights clarified in case of a risk encounter. Users also get the option to contradict.
Tracing solutions also comply with current data protection regulations such as GDPR, as employers may only process employee data after employees have given their prior consent for the intended purpose.
2
Are people tracked when contacts are digitally traced?
No. While tracking collects location data from users, contact tracing only records contacts that are less than a defined distance away.
With the UWB technology, which has proven itself in business solutions, the collection of location data would only be possible with a so-called “anchor network”.However, since this is not part of contact tracing products, tracking movements is technically not possible.
3
Is contact tracing technology used to collect data?
No. Specialized digital technologies for contact tracing have been developed according to the principles of “Privacy by Design” (data protection is already taken into account during the development of a data processing procedure and not after the development is completed) and “Privacy by Default” (factory settings of a development are preset to the strictest possible protection of personal user data in the default setting).
On the one hand, this means that as a matter of principle, only data that is necessary for the purpose of contact detection and evaluation is collected. On the other hand, it is ensured that personal data is only processed when people need to be informed for their own protection and for the protection of others.
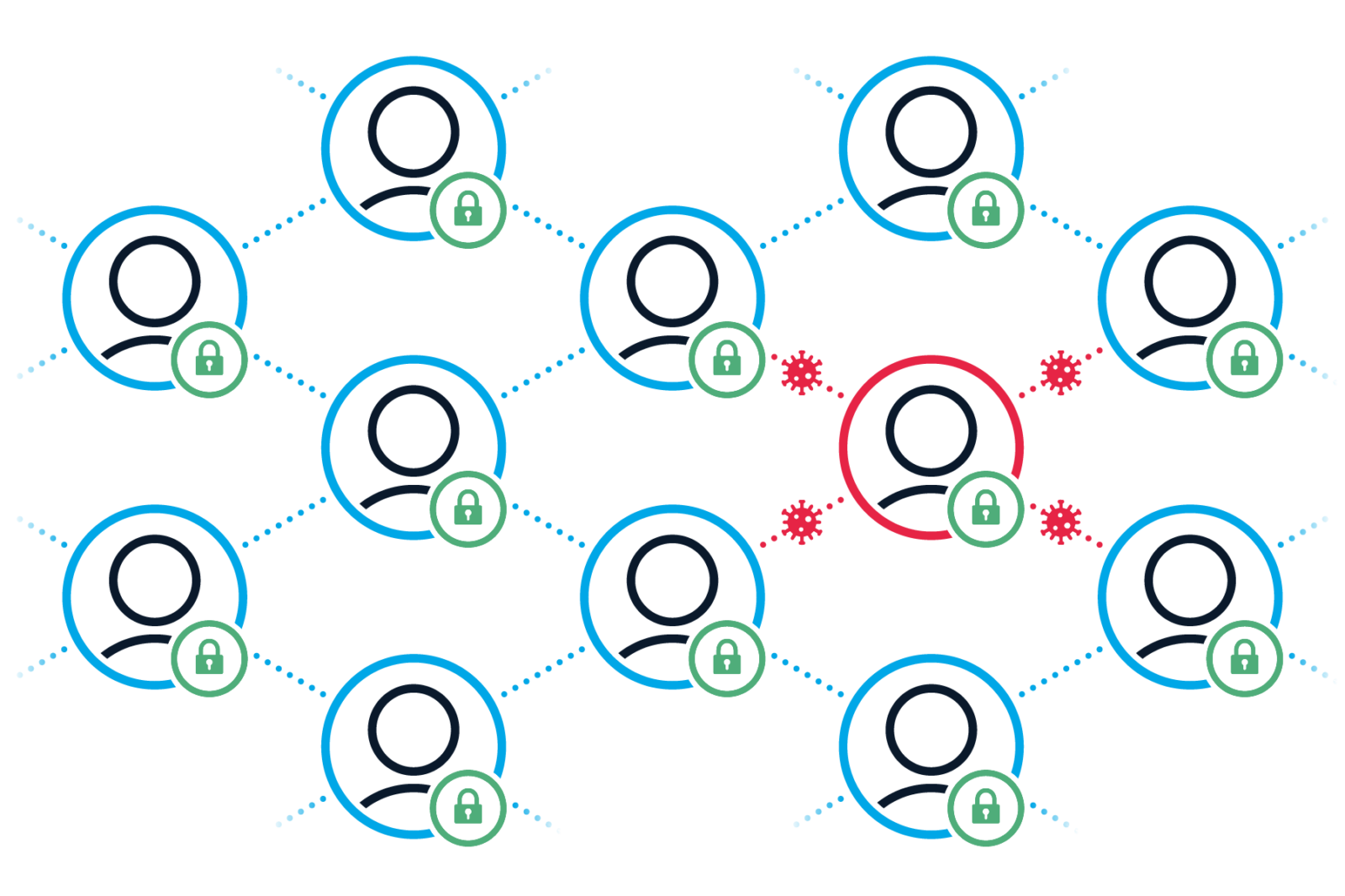
Data protection is important — and so is seamless contact tracing
Particularly in indoor areas, where the risk of contracting the highly infectious coronavirus is particularly high, digital contact tracing provides reliable information on whether other people may have become infected and whether and who should be tested and sent into quarantine.
However, even during an exceptional situation such as the ongoing coronavirus crisis, the principles of “Privacy by Design” and “Privacy by Default” as well as the best possible data protection must be guaranteed.
Our advice: Customization is key
Digital solutions for contact tracing enable users to evaluate the risk of infection of each individual contact without interference and with centimeter precision, even in complex rooms.
In addition to the distance, the duration of contact, the alignment of people to one another, and other protective measures taken, such as protective screens or masks, can also be taken into account.
Factors like these vary from environment to environment. It is therefore advisable to determine all truly purpose-oriented and thus relevant information before implementation. Close coordination with employees or work councils also ensure that the protection of personal data is not diluted in the process.
In this way, companies remain able to act even in the event of an infection, protect their processes and at the same time provide employees with the best possible protection — both in terms of health and data protection.














