UWB Technology
UWB in iPhone, Apple Watch, and Against COVID-19: Everything You Need to Know About the Technology
With the increasing integration of ultra-wideband (UWB) sensors in consumer electronics like Samsung phones or Apple watches, UWB technology is poised to take over the localization market. Beyond consumer electronics, what are the advantages of UWB for industrial or retail applications? How can ultra-precise indoor positioning through cost-efficient UWB solutions like the KINEXON X‑Tag optimize supply chains, material flow, or industrial automation? Find out here.

What Is Ultra-Wideband Technology (UWB)?
Ultra-wideband (UWB) is a radio-based communication technology for short-range use and fast and stable transmission of data. Thanks to its unrivaled precision, transmission speed, and reliability, UWB is often the technology of choice for indoor localization of moving assets in complex and space-sensitive environments.
UWB is considered the gold standard of indoor localization technologies thanks to its numerous advantages over comparable technologies such as RFID, BLE or WiFi. It is an ideal solution for location-based automation.
Why UWB? A Localization Technology Comparison


Price Revolution in the UWB Market
With the X‑Tag to the Smart Factory: The world’s most cost-efficient UWB sensor now enables location-based industrial automation.

Spotlight: Industry Challenges UWB Helps Solve

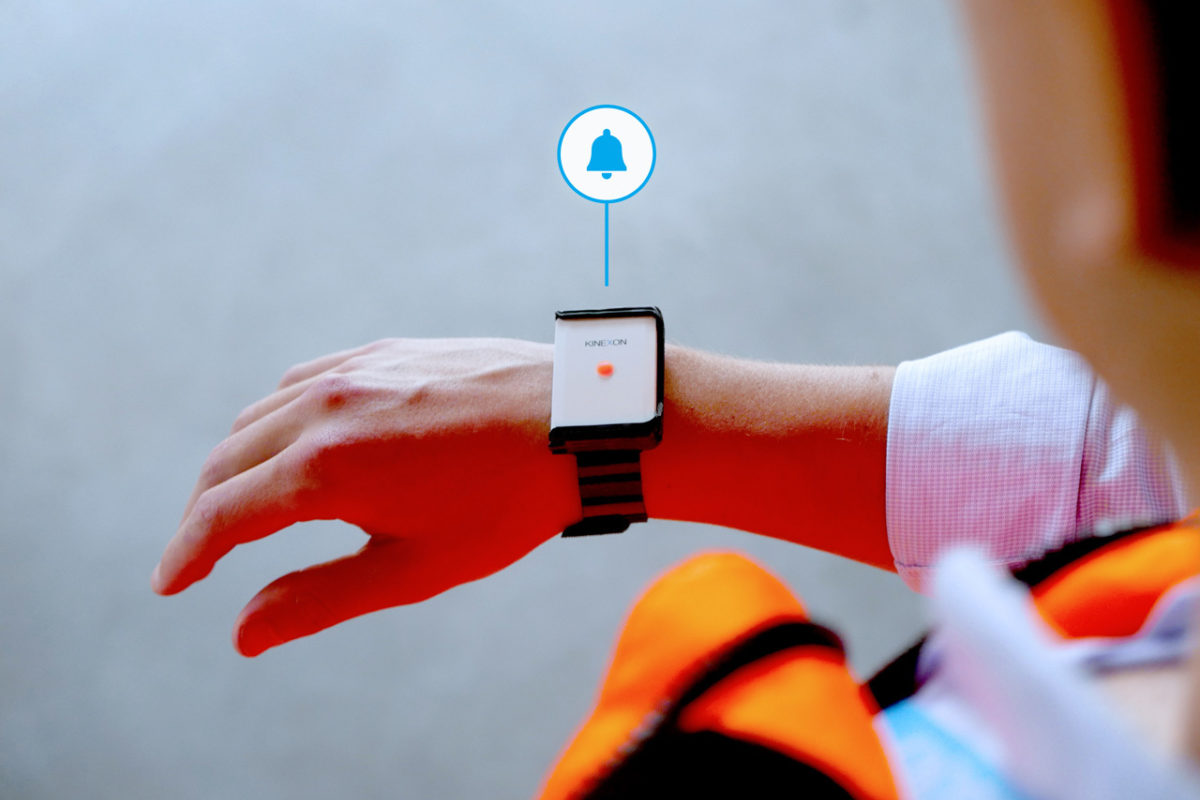
High Search Times and Inefficiencies
Explore the KINEXON X‑Tag, the world’s most affordable UWB sensor for indoor asset tracking, track & trace, and material flow automation.

Lack of Documentation and Sustainability
Explore the KINEXON ePaper-Tag for a full digital thread to satisfy quality assurance and sustainable, paperless production.

Error-Prone Manual Processes
KINEXON’s RTLS solutions and its powerful location-based automation software allow you to fully leverage the benefits of UWB.
Current News: UWB Today
KINEXON & UWB-Standards

Pioneering UWB-Solutions
KINEXON is a proud member of FiRa Consortium, UWB Alliance and Omlox, who promote the use of UWB and create standards for the technology.
UWB in Detail: Technical Specifications
From the first attempts to transmit messages wirelessly to the invention of the “telemobiloscope” in 1902, today’s UWB technology looks back onto vast utilization for localization.
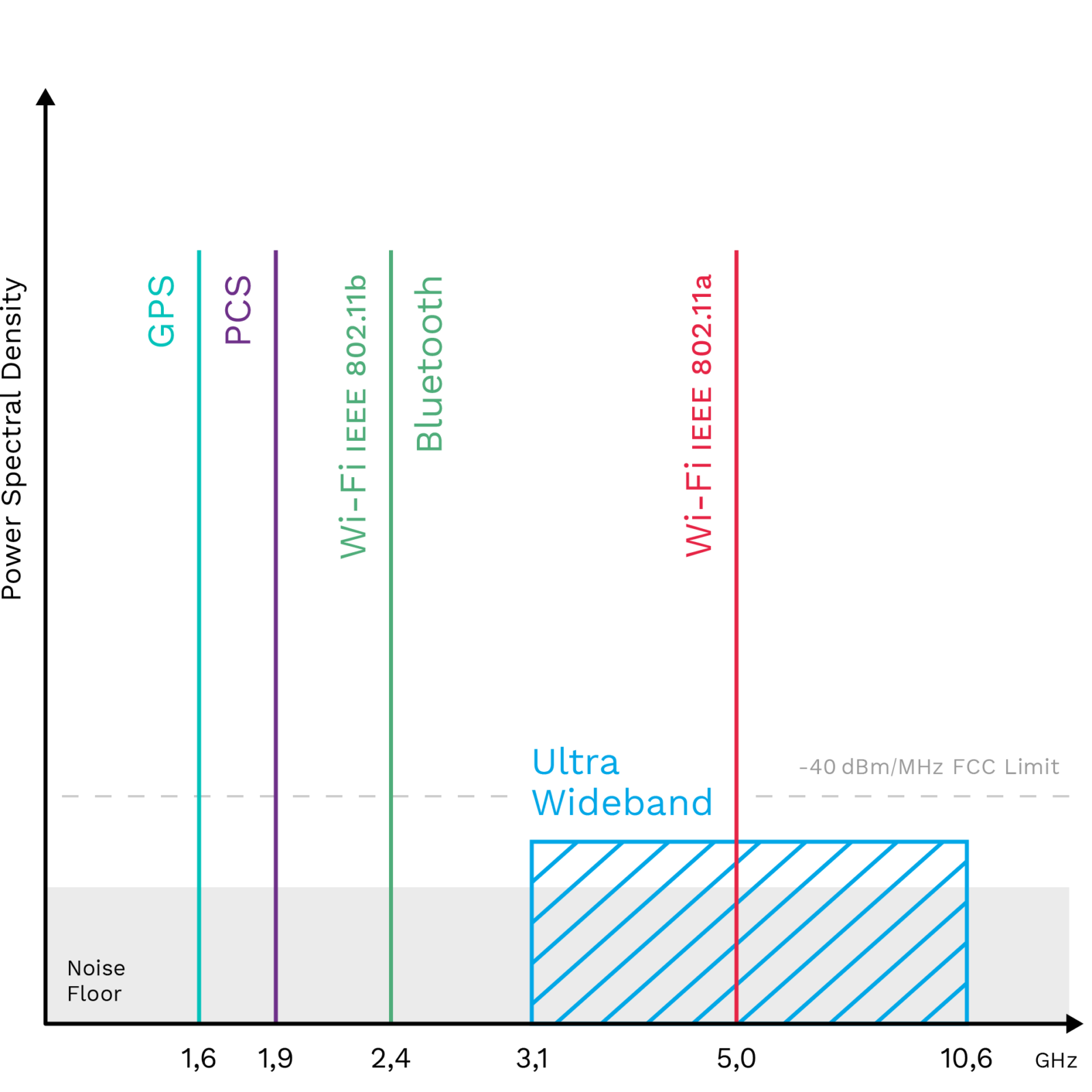
Despite its long history, there are still countless of opportunities to leverage the technology’s potential. Unlike other technologies, it is not tied to any frequency. In addition, UWB can transmit data over an extremely wide frequency spectrum and can utilize unused frequency capacities. The UWB frequency range is at least 500 MHz. For comparison: WLAN channels are only about 1/10th as wide.
Facts & Figures
- Frequency range: 3.1−10.6 GHz
- Propagation speed: linear speed of light (0.3 m/ns)
- max. data rate: 480 Mbits/s
- max. transmission power: <1 mW
- range: 10 – 200 m (32.8−656.2 ft.) (depending on application)
- Localization accuracy: 0.1−0.5 m (0.33−1.64 feet)
- low susceptibility to interference (no interference with WLAN and ISM channels)
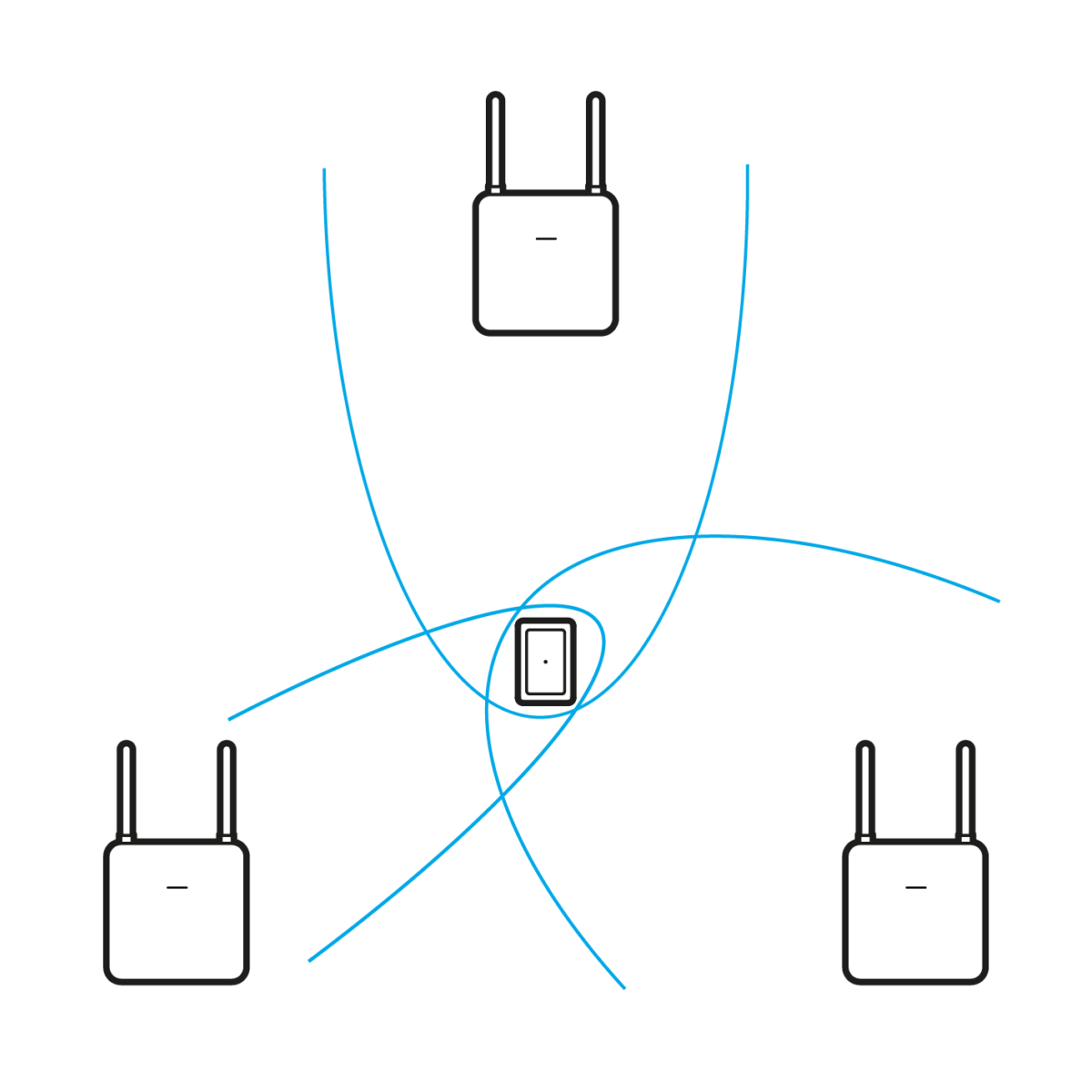
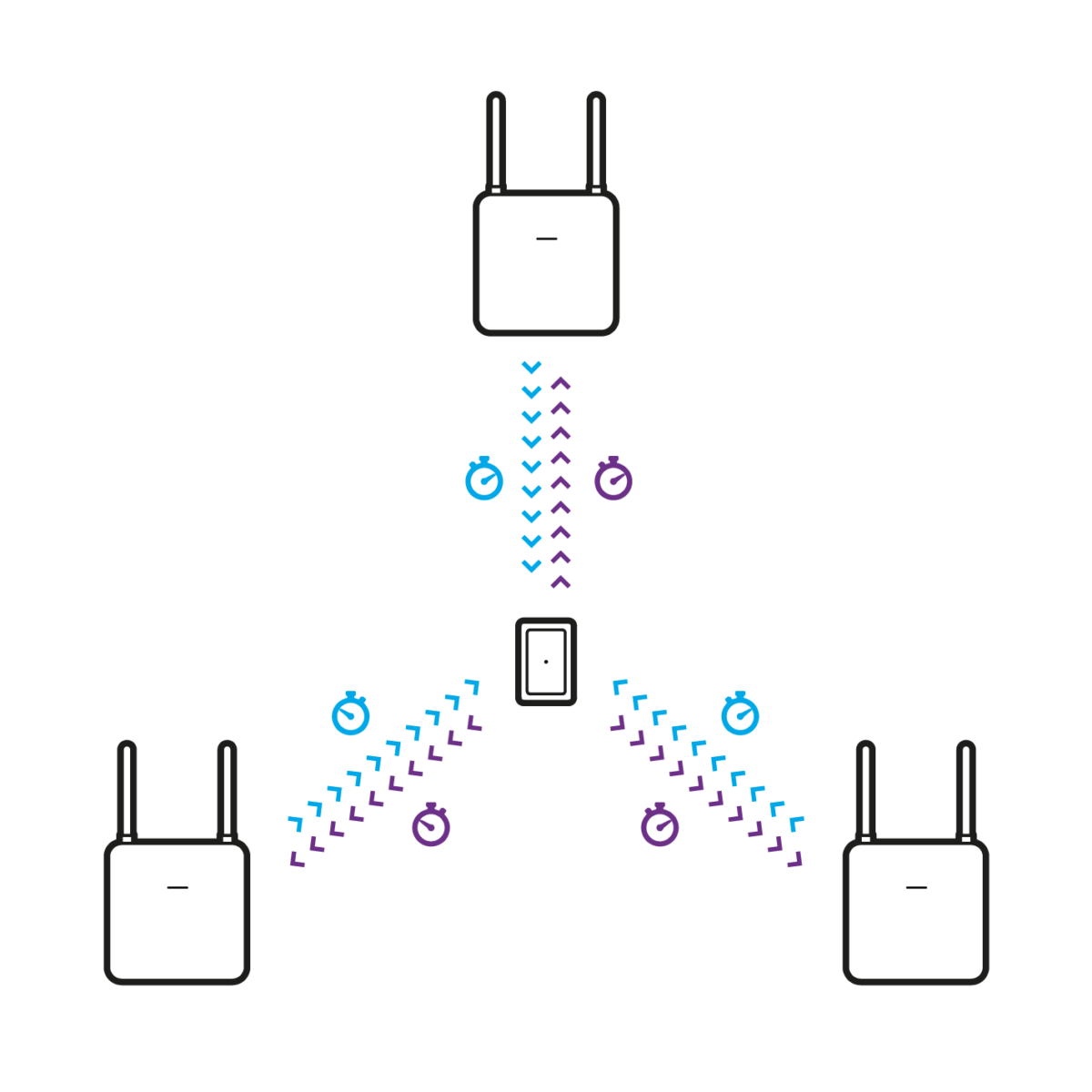
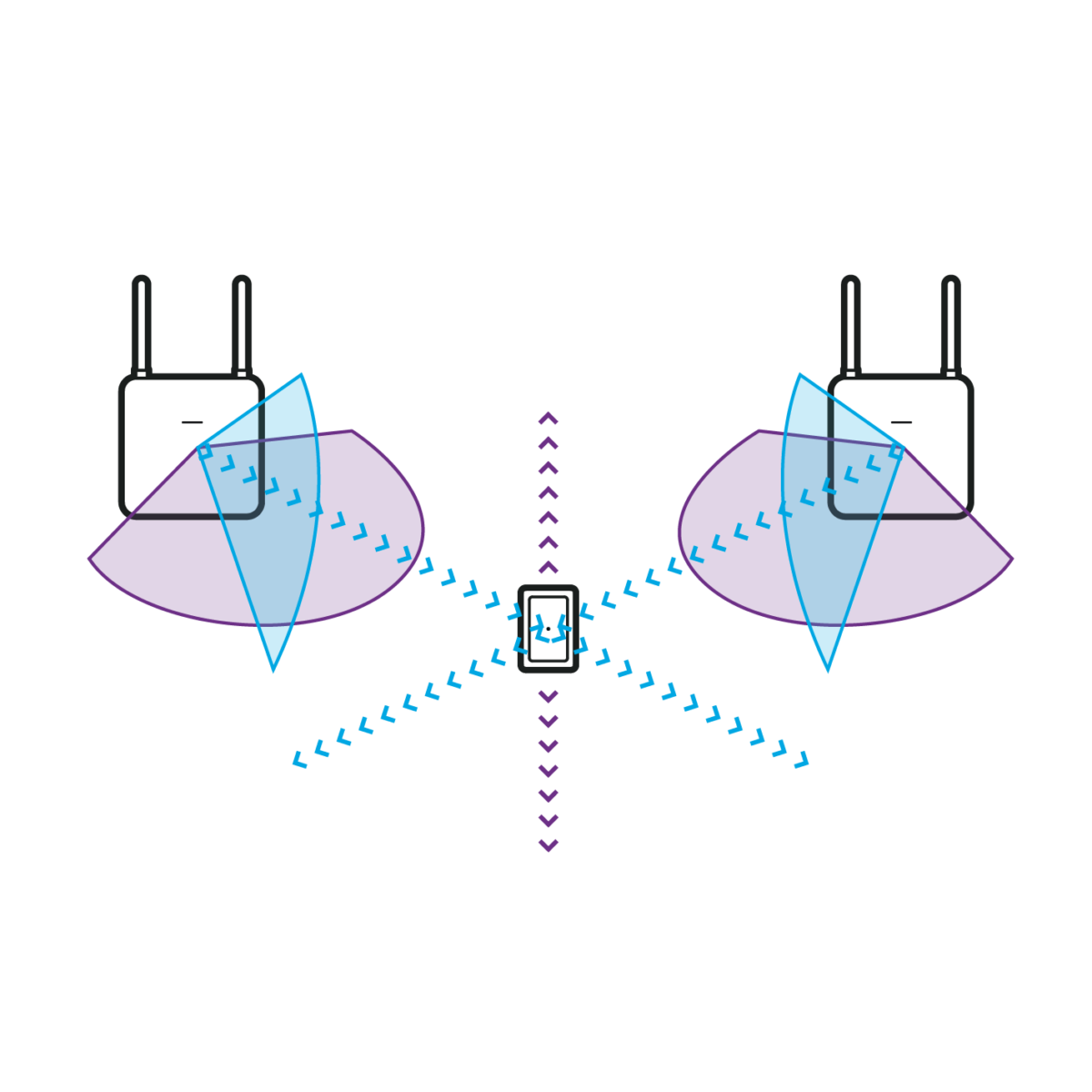
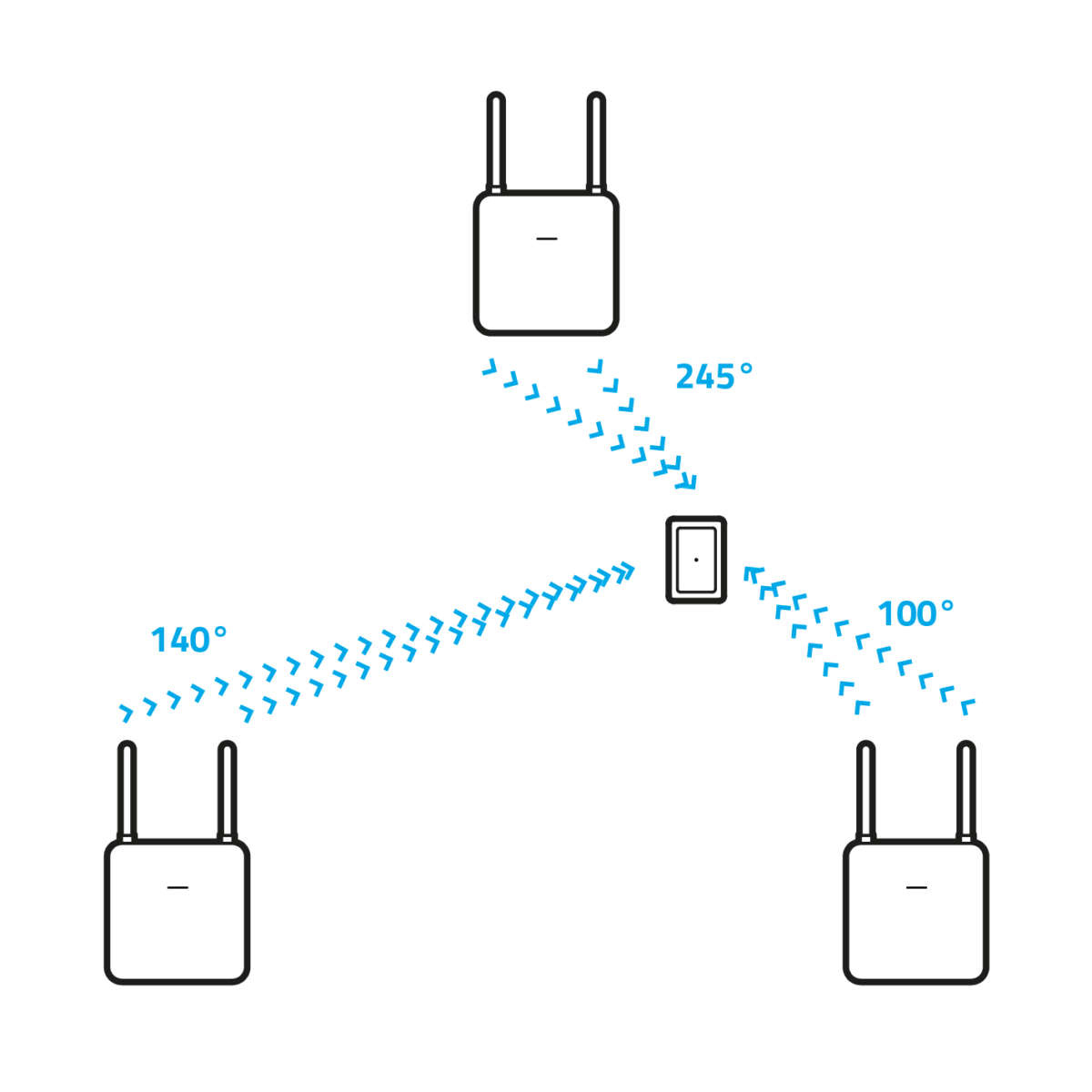
- Localization via transit time procedure (ToF, “Time of Flight“)